БИОМЕДИЦИНСКИЕ АСПЕКТЫ ИММУНОЛОГИИ
The article gives an overview of the main areas of fundamental and applied research related to the issues of immunology and cell engineering. The goals and objectives of the Center for Immunology and Allergology established at the Institute of Biophysics and Cell Engineering of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus are outlined.
Cellular therapy develops rapidly throughout the world. The list of diseases of various etiologies that are treated with biomedical cellular products is constantly growing. The Center for Immunology and Allergology was opened in the The Institute of Biophysics and Cell Engineering of National Academy of Science of Belarus in 2021. Since that the developing of new biomedical cell products for the correction of immunopathological conditions was started in collaboration with the Belarusian State Medical University. The technologies for producing of biomedical cellular products based on cytokine induced killer cells for the treatment of oncological diseases of the urogenital area, tolerogenic dendritic cells for the treatment of type 1 diabetes, and regulatory T lymphocytes for the treatment of sclerosis were developed.
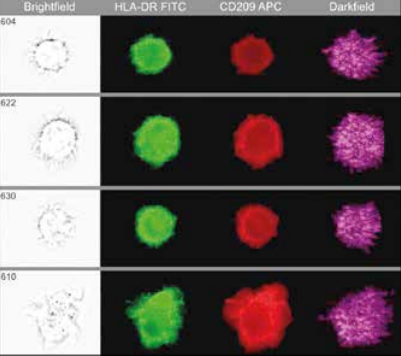
The advanced analysis of immune parameters describing differentiation profile, activation and exhaustion of lymphocytes, monocytes and granulocytes of patients with moderate and severe/critical COVID‑19 pneumonia was performed.
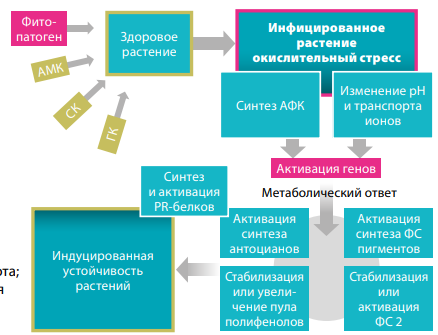
The author considers modern concepts of plant immunity, defining the main mechanisms of the defense reactions priming in a pathological process with the participation of natural inducers of resistance and the ways of their implementation in plants.
INNOVATION ECONOMY
The author presented his overview of the main areas of fundamental scientific research in Belarus’ economics at the present stage.
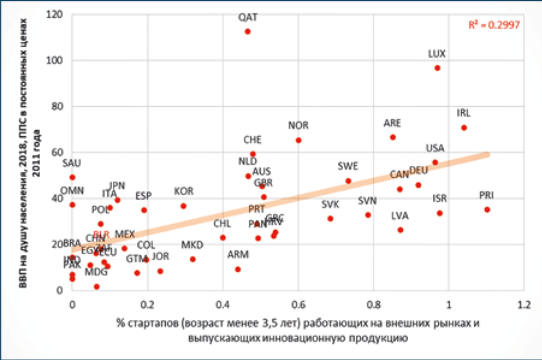
The authors presented the concept of "hidden champions", i. e. small and medium-sized technological enterprises that are world leaders in their niches. The development ways and factors of the Belarusian companies in this category are analyzed.
DIGITAL PERSPECTIVE
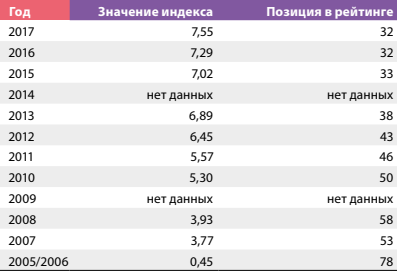
Economic research in recent years has emphasized the need to analyze the development of a particular area through the prism of inter‑ relation with other areas. Despite the widespread introduction and applica‑ tion of information and communication technologies (ICT), the relationship of this sector with institutional development is not fully described. The article is devoted to the issue of the influence of the sphere of information and communication technologies on the institutional development of na‑ tional economies. The relationship between the level of development of the ICT sector and the institutional development of the country was established on the basis of a statistical analysis of the key development indices of the above categories. A list of key directions of economic policy of the Republic of Belarus has been formed with the aim of forming and developing an efficiently functioning ICT sector.
The article justifies the current approaches to the digital transformation of the Belarusian energy system analysis. The authors suggested a method, which allows taking into account both technical and economic factors of the electric power industry digitalization.
HERITAGE
On the basis of numerous scientific expeditions there has been studied one of the most common folk calendar feasts in Belarus, its historical and spiritual origins, rites, beliefs and signs.
BIODIVERSITY
There was presented the unique development of Belarusian scientists, which allows specialists to quickly receive the necessary information about flora objects on the territory of our country and more efficiently manage its natural resources.
DISSERTATION RESEARCH
High lethality in peritonitis and the data about the role of nitric monoxide in its pathogen‑ esis, determines the feasibility of the research to study effects of the NO‑synthase substrate – L‑arginine. The aim of the research was to study the acute experimental peritonitis course in rats with administration of the NO‑synthase substrate – L‑arginine. The experiments were carried out on male rats, divided into 3 series and intraperitoneally injected with: series 1 (control) – 0,9% sodium chloride, series 2 (experi‑ mental peritonitis) – 15% fecal suspension, 0,6 ml/100 g, series 3 (EP+L‑Arg) – 15% fecal suspension, 0,6 ml/100 g, followed by intramuscular administration of L‑arginine, 300 mg/kg. Administration of the NO‑synthase substrate – L‑arginine to rats with experimental peritonitis had a corrective effect in the form of a decrease in the severity of intoxication syndrome, the reaction of leukocytes of blood and peritoneal fluid, changes in nitrites/nitrates level, a decrease in the activity of oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction and the degree of damage to peritoneum.
ISSN 2412-9372 (Online)